Does Adverse Possession Continue if Title Transfers
Adverse Possession
A legal principle that states that a person can acquire legal ownership of someone else's property
What is Adverse Possession?
Adverse possession is a legal principle that states that a person can acquire legal ownership of someone else's property. In order to do so, they need to acquire possession or reside on that property for a certain length of time. Typically, the form of property is land.

If the adverse possession is successful after following certain requirements and conditions, there will be no requirement to compensate the owner for that property or receive their permission. Adverse possession is also known as squatter's rights.
Summary
- Adverse possession is a legal principle that states that a person can acquire legal ownership of someone else's property. The idea of adverse possession is important because it ensures that land is used efficiently.
- England's 2002 Land Registration Act states that if the land is unregistered for ten years, the adverse possessor can apply to become the new registered owner.
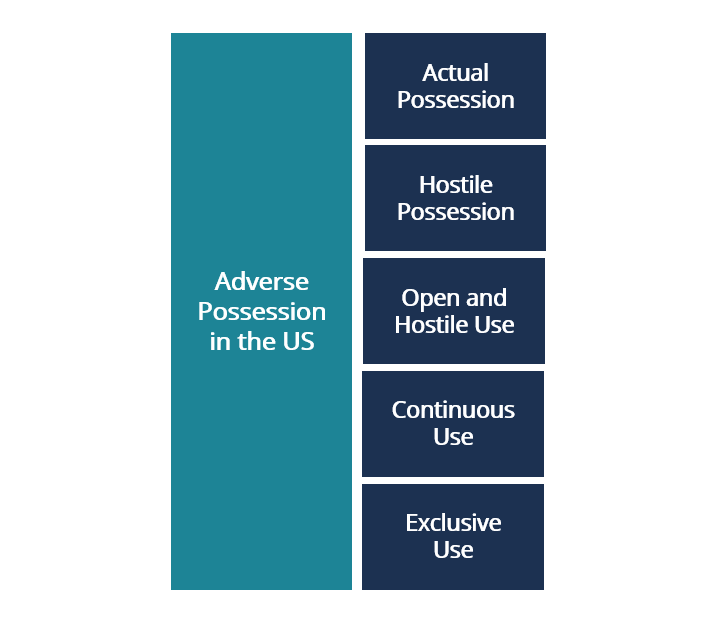
- In the United States, five conditions, at minimum, need to be met – actual possession, hostile possession, open and notorious use, continuous use, and exclusive use.
How Adverse Possession Works
The rights and conditions for achieving adverse possession vary depending on the country. For example, in the US, there are five main conditions that the adverse possessor must follow to be successful in claiming ownership of someone else's property.
During the process of adverse possession, the original owner can recover possession of their property through legal action. English law states that if the original owner does not exercise their rights and attempt to recover their property within a certain time period, they will lose that right, and the adverse possessor becomes the property's owner.
Over the years, however, legislation's changed the lengths of the rules. For example, in the US, the time available to the original owner varies between three and forty years, depending on the particular state.
It is important to note that personal property can also be adversely possessed. However, the rules in such a situation are stricter and typically favor resides with the legal owner. An example of personal property that sometimes faces adverse possession is a work of art.
Adverse Possession in England
Following the passage of the Land Registration Act 2002 in England, it is becoming a bit more difficult to initiate adverse possession. The law states that if the land is unregistered for ten years, the adverse possessor can apply to become the new registered owner. From there, the registrar notifies the person who is the registered titleholder at that time.
If the registered titleholder does not attempt to reject the adverse possessor for two years, then the title can be transferred. The law made it so that people would not lose the title without being made aware of the situation.
Adverse Possession in the United States
In order to acquire adverse possession, there are five conditions, at a minimum, that need to be met. However, some states have added additional conditions.
- Actual Possession: The adverse possessor must physically use the land, not just walk on it, i.e., mowing or harvesting.
- Hostile Possession: The adverse possessor must have used the land without the permission of the original owner.
- Open and Notorious Use: The adverse possessor must utilize the property in a way that they can be seen. It is so the original owner can potentially come to the conclusion that someone may start a claim.
- Continuous Use: The adverse possessor needs to hold the property continuously throughout the period.
- Exclusive Use: The adverse possessor needs to be the exclusive user. If, during the period the original owner uses the land, adverse possession cannot be claimed.
Importance of Adverse Possession
Adverse possession is important to understand because, as a property owner, you need to be aware of what can happen if you are not utilizing your land. In addition, if you are interested in a particular property, having knowledge regarding the regulations of an unused property may be beneficial if you want to become the legal owner.
Overall, the idea of adverse possession is important because it ensures that the land is used efficiently. If a legal owner is not making use of the property and it is becoming deserted, someone willing should have the ability to take over the land and utilize it efficiently.
Practical Example
You notice a particular area of land has been untouched for more than ten years. You decide that you would like to acquire legal ownership of the land and put it to good use by harvesting on that land.
In order to be successful, you look up whether there are any extra conditions on top of the five basic conditions you need to meet in order to achieve adverse possession. Additionally, you need to look up the law for your area to determine how long the original legal owner has to reject your attempt to own the property.
Additional Resources
CFI is the official provider of the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™ certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst.
To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below:
- Contingent Beneficiary
- Escheatment
- Marital Property
- Probate
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/other/adverse-possession/
Post a Comment for "Does Adverse Possession Continue if Title Transfers"